Selling your business is a really big decision for any owner and it requires careful planning and understanding of its true worth For Indian entrepreneurs considering an exit, accurately valuing your business is crucial to ensure you receive a fair price and make informed decisions. This guide provides a step-by-step approach to valuing your business, tailored to the Indian market context.
1. Understanding Business Valuation
Business valuation is a process of determining the fair value value of a business or company. It is crucial for various purposes including mergers and acquisition (M&A), investment analysis, ESOPs planning, , fundraising, financial reporting and getting true value of selling a business. In India, business valuation is particularly important due to diverse economic landscape and regulatory environment.
2. Common Valuation Methods
Several methods are used to value a business, each suitable for different types of businesses and circumstances:
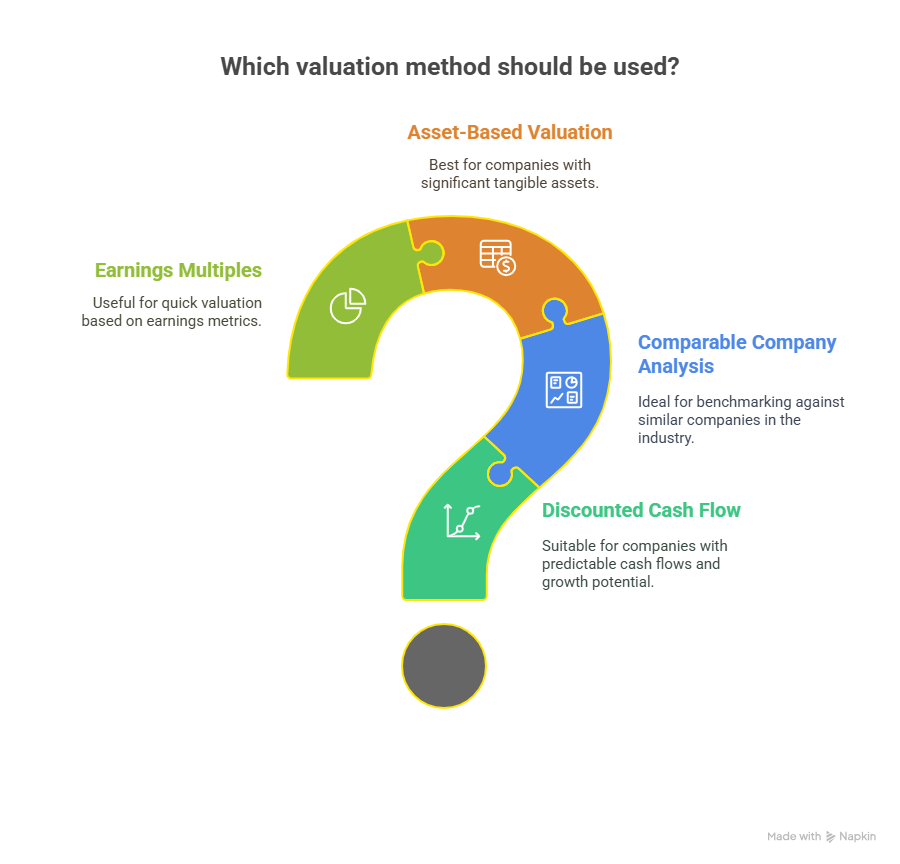
1. Discounted Cash Flow (DCF) Method:
This method estimates the value of a business based on its expected future cash flows, adjusted for the time value of money. It is particularly useful for businesses with predictable and stable cash flows.
Example:
You expect your business to earn ₹50 lakhs each year for 5 years.
If we adjust for inflation and risk (using a 10% discount), the total value today would be around:
👉 ₹1.90 crore
This method helps you understand the true value of future income in today’s money.
2. Comparable Company Analysis (CCA):
This approach involves comparing the business to similar companies in the same industry that have been sold recently. Key financial metrics such as revenue, EBITDA, and profit margins are used to establish valuation multiples.
Example:
Businesses like yours are selling for 5 times their yearly profit.
If your yearly profit is ₹50 lakhs:
Your business could be worth ₹5 Crores (₹50L × 5)
Great when buyers or investors want to compare “apples to apples.”
3. Asset-Based Valuation:
This method calculates the value of a business by determining the net asset value (NAV), which is the total assets minus total liabilities. It is commonly used for asset-heavy businesses.
Example:
You own ₹30 lakhs worth of equipment and property. You owe ₹10 lakhs.
👉 Your business is worth ₹20 lakhs (₹30L – ₹10L)
Best for manufacturing, real estate, or any asset-heavy business.
4. Earnings Multiples (EBITDA or SDE):
This approach applies a multiple to the company’s earnings before interest, taxes, depreciation, and amortization (EBITDA) or Seller’s Discretionary Earnings (SDE). The multiple is typically derived from industry standards or comparable transactions.
Example:
Your business makes ₹20 lakhs in profit (EBITDA).
Buyers in your industry pay 4 times that.
👉 Your business is worth ₹80 lakhs (₹20L × 4)
Quick, market-driven, and commonly used in actual business sales.
3. Key Factors Influencing Valuation
Several factors can impact the valuation of a business:
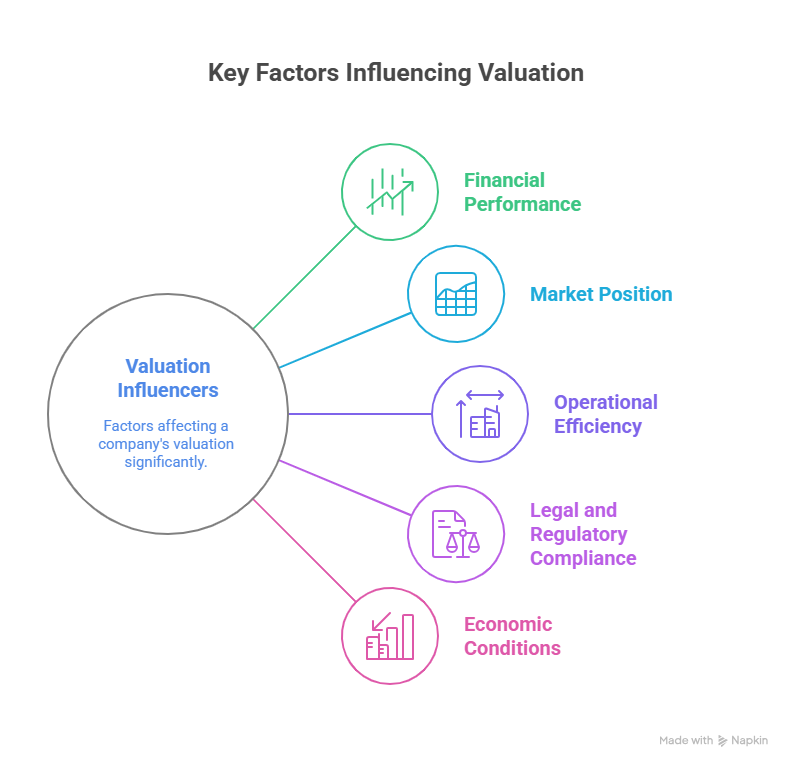
1. Financial Performance:
Consistent revenue growth, profitability, and strong cash flows enhance a business’s value.
2. Market Position:
A strong brand, customer loyalty, and competitive advantage place a business in a favorable position for increased valuation.
3. Operational Efficiency:
Investments in streamlined processes like effective management systems and scalable business models have a positive impact on operational efficiency of the firm, which aids in enhancing valuation.
4. Legal and Regulatory Compliance:
Local laws and tax compliance along with industry benchmarks are essential to achieving higher valuation.
5. Economic Conditions:
The overall economic environment, including interest rates and market trends, can influence business value.
4. Valuation in the Indian Context
While valuing businesses in India, business valuation must consider unique factors such as:
1. Regulatory Environment:
Compliance with Indian laws such as GST regulations and the Companies Act alongside labor law obligations is important from a valuation standpoint.
2. Market Dynamics:
Familiarity with regional economic conditions such as market trends and consumer behavior is essential.
3. Tax Implications:
Awareness of capital gains tax, GST on business sales, and other tax considerations is necessary for accurate valuation
5. Steps to Value Your Business
To fairly value your business, follow these steps:
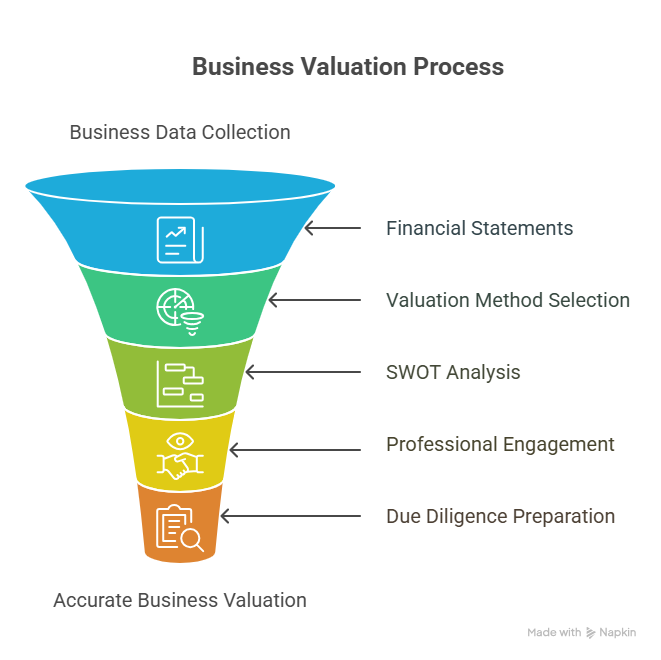
1. Gather Financial Statements:
Collect cash flow statements, balance sheets, profit and loss statements for the past 3-5 years.
2. Choose an Appropriate Valuation Method:
Select a valuation method that aligns with your business type and industry standards.
3. Conduct a SWOT Analysis:
Assess your business’s strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats to understand its position in the market.
4. Engage Professionals:
Consider hiring financial advisors, accountants, or valuation experts to ensure an accurate assessment.
5. Prepare for Due Diligence:
Organize all necessary documents and information to facilitate the due diligence process for potential buyers.
6. Common Mistakes to Avoid
Avoid these pitfalls when valuing your business:
1. Overestimating Value:
Inflating the business’s worth can deter potential buyers.
2. Neglecting Intangible Assets:
Overlooking the value of intellectual property, brand reputation, and customer relationships can lead to undervaluation.
3. Ignoring Market Conditions:
Failing to consider current market trends and economic conditions can result in unrealistic valuations.
4. Lack of Transparency:
Hiding liabilities or financial issues can erode trust with potential buyers.
Final Thought
Accurately valuing your business is a critical step in the selling process. By understanding the various valuation methods, considering key factors, and being aware of common mistakes, you can ensure a fair and informed sale. For Indian entrepreneurs, it’s advisable to seek professional assistance to navigate the complexities of business valuation and achieve the best possible outcome.

6 thoughts on “How To Accurately Value Your Business For Sale in India”